Introduction to Zeolites
Zeolites are fascinating materials with a unique structure of tiny pores and channels. They are widely used in industries for applications like catalysis, adsorption, and ion exchange. One of the most effective methods to synthesize zeolites is hydrothermal synthesis, which involves the use of a special device called a hydrothermal autoclave.
What is a Hydrothermal Autoclave?
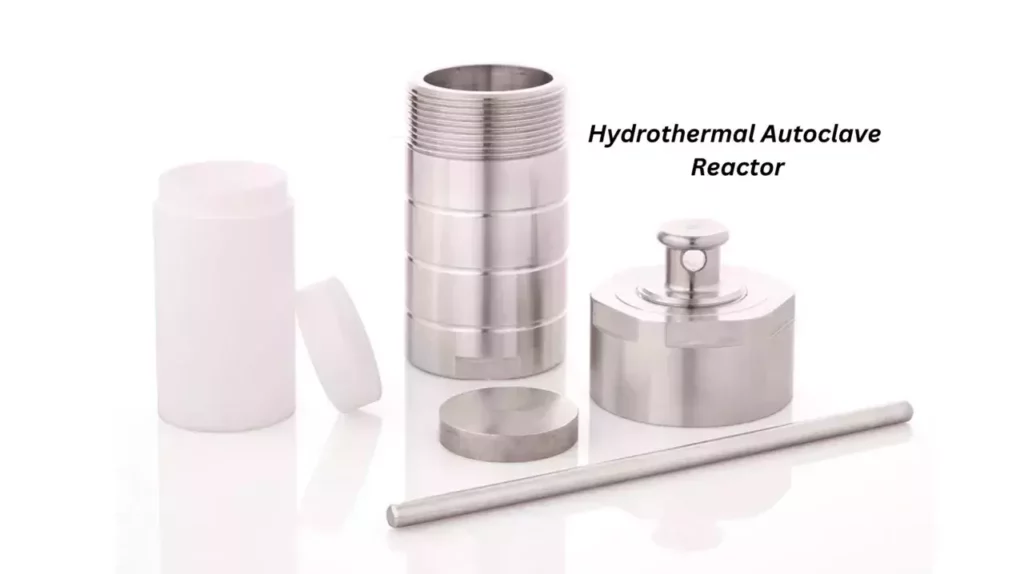
A hydrothermal autoclave is a high-pressure, high-temperature vessel that conducts chemical reactions involving water as a solvent. It can withstand in extreme conditions, which makes it ideal for synthesizing materials like zeolites that require such environments.
How Does Hydrothermal Synthesis Work?
Hydrothermal synthesis mimics the natural processes deep within the Earth, where minerals are formed under high pressure and temperature. In a laboratory setting, a hydrothermal autoclave creates similar conditions to facilitate the formation of zeolites.
- Preparation of the Reaction Mixture: The process begins by mixing raw materials, such as silicon and aluminum sources, with a solvent (usually water) to form a gel-like mixture.
- Loading the Autoclave: This mixture is then placed into the hydrothermal autoclave, which is sealed tightly to ensure no gases or liquids can escape during the reaction.
- Heating and Pressurizing: The autoclave is heated to a high temperature, often between 100°C to 200°C (212°F to 392°F). As the temperature rises, the pressure inside the autoclave also increases. These conditions are crucial for the formation of zeolites.
- Crystallization: Under these high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, the raw materials react and slowly crystallize into zeolites. Depending on the desired zeolite structure, this process can take several hours to several days.
- Cooling and Recovery: After the reaction, the autoclave is allowed to cool down before opening. The newly formed zeolites are then collected, washed, and dried for further use.
Why Use Hydrothermal Autoclaves for Zeolite Synthesis?
- Controlled Environment: Hydrothermal autoclaves provide a controlled environment where temperature and pressure can be precisely managed, ensuring consistent and high-quality zeolite synthesis.
- Enhanced Purity and Crystallinity: The extreme conditions within the autoclave promote the formation of highly pure and well-defined crystalline zeolites.
- Versatility: This method allows for synthesizing various zeolite structures by adjusting the reaction conditions and raw materials.
Applications of Hydrothermally Synthesized Zeolites
- Catalysis: Zeolites are widely used as catalysts in chemical reactions, including oil refining and petrochemical processes. Their unique structure allows for efficient and selective catalysis.
- Adsorption: Zeolites can adsorb gases and liquids, making them useful in applications like gas purification, water softening, and air filtration.
- Ion Exchange: Zeolites can exchange ions with their environment, which is beneficial in water treatment processes to remove harmful ions and replace them with more desirable ones.
Conclusion
Hydrothermal autoclaves play a crucial role in synthesizing zeolites, providing the conditions for their formation. This method ensures high-quality zeolites and allows for the creation of various zeolite structures, enhancing their applicability in numerous industrial processes. As research continues, hydrothermal autoclaves in material synthesis promise to unlock even more advanced and versatile zeolite applications.
To purchase,Hydrothermal Autoclaves,please follow these links.
1- Techinstro
2- Shilpent