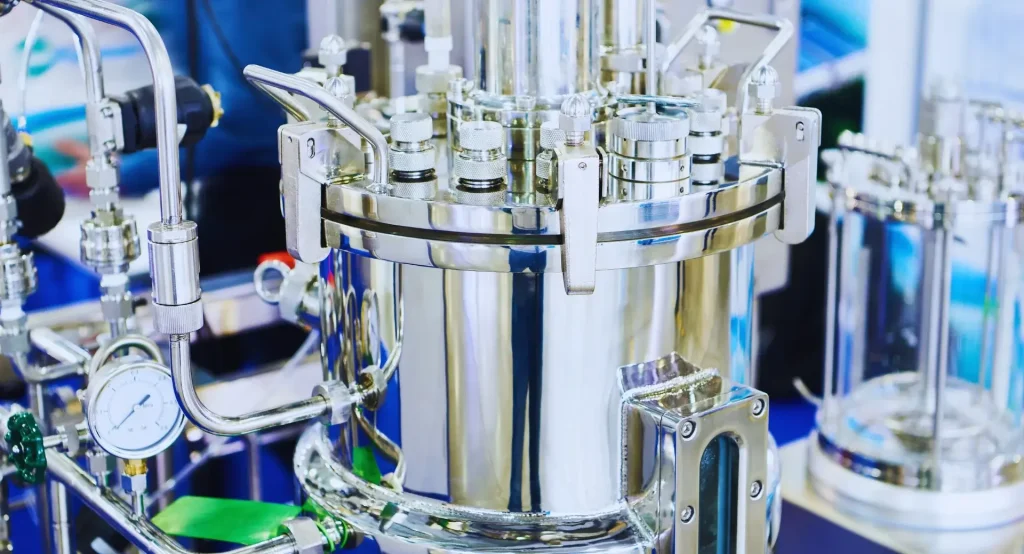
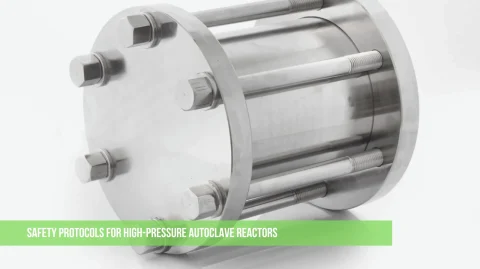
The high-pressure autoclave reactor is an essential tool in scientific research, chemical synthesis, and material development. It operates under high pressure and temperature, making the choice of material for its body critical for safety, durability, and performance.
What Is the Reactor Body Made Of?
The reactor body is the main part of the autoclave, responsible for containing the reaction and resisting extreme conditions. It must be made from a material that can handle:
- High Pressure: Withstand forces exerted by gases and liquids under pressure.
- High Temperature: Resist thermal expansion and heat-related degradation.
- Corrosion: Withstand exposure to reactive chemicals and prevent deterioration over time.
Buy High-Pressure Autoclave Reactor
Common Materials of Construction (MOC)
Stainless Steel
Why It’s Used: Stainless steel is strong, corrosion-resistant, and affordable.
Grades:
- SS316: Commonly used for autoclave bodies due to its good resistance to chemicals and high temperatures.
- SS304: Less corrosion-resistant than SS316 but suitable for moderate environments.
Best For: General laboratory use, moderate temperatures, and pressures.
Hastelloy
- Why It’s Used: Hastelloy is highly resistant to chemical corrosion, especially from strong acids and oxidizing agents.
- Advantages: Maintains strength and integrity under high temperatures.
- Best For: Applications involving harsh chemicals or high-temperature processes.
Titanium
- Why It’s Used: Titanium is lightweight, exceptionally corrosion-resistant, and durable.
- Advantages: Performs well with seawater, chlorine, and other aggressive substances.
- Best For: Specialized industries like pharmaceuticals, marine research, and aerospace.
Inconel
- Why It’s Used: Inconel is a nickel-based alloy known for its ability to handle extreme heat and chemical exposure.
- Advantages: Excellent performance in high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
- Best For: Very high-pressure environments and processes requiring maximum durability.
Carbon Steel
- Why It’s Used: Carbon steel is strong and cost-effective but less corrosion-resistant.
- Best For: Basic applications where corrosion is not a significant concern.
Which MOC Is Good, and Which Is Best?
Good Options:
- Stainless steel (SS316) is a reliable choice for most laboratory and industrial purposes due to its balance of cost, strength, and corrosion resistance.
Best Option:
- For highly demanding environments, Hastelloy or Inconel is ideal. These materials can handle the harshest chemicals and highest pressures without compromising safety.
Factors to Consider When Choosing MOC
- Type of Reaction: Corrosive chemicals require highly resistant materials like Hastelloy or Titanium.
- Operating Pressure and Temperature: Higher pressure and temperature demand stronger alloys like Inconel.
- Budget: Stainless steel is more affordable, while advanced materials like Hastelloy and Titanium are premium.
- Longevity: Choosing the right material reduces maintenance and replacement costs in the long run.
Conclusion
The construction material for a high-pressure autoclave reactor body depends on the specific application. Stainless steel is a good all-around option, but Hastelloy, Titanium, or Inconel are the best choices for challenging environments. Always consult with experts to select the right MOC for your requirements, ensuring safety and efficiency in your processes.