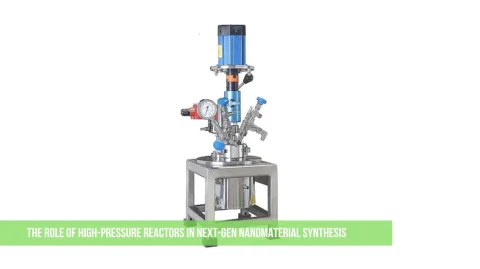
A hydrothermal autoclave is a special type of pressure vessel used in laboratories for synthesizing materials under high temperatures and pressure. It is mainly used in chemical and material science research to create nanomaterials, crystals, and compounds that require a controlled environment.
Let’s explore how a hydrothermal autoclave works step by step.
Main Parts of a Hydrothermal Autoclave
Before understanding its working, let’s look at the key components inside the autoclave:
- Outer Shell: Made of stainless steel, this is the main body that holds everything together.
- Teflon or PTFE Liner: A chemical-resistant inner container where the reaction occurs.
- Lid & Seal: Ensures the vessel is airtight and can handle high pressure.
- Screw Cap or Locking Mechanism: Helps secure the lid tightly to prevent leaks.
Buy Hydrothermal Autoclave Reactors from verified suppliers and manufacturers:
How Does a Hydrothermal Autoclave Work?
The hydrothermal autoclave creates high-pressure and high-temperature conditions inside a sealed environment. This allows reactions to occur that would otherwise be difficult under normal conditions.
Step-by-Step Process
Step 1: Preparing the Solution
Scientists prepare a chemical solution that needs to undergo a reaction. This may include water and different chemical precursors.
Step 2: Filling the Liner
The solution is poured into the Teflon liner or PTFE chamber. The liner is never filled—usually, around 70–80% of its total volume is used. This leaves space for expansion when heated.
Step 3: Sealing the Autoclave
Once the solution is inside:
- The Teflon liner is closed with its cap.
- The liner is placed inside the outer shell of the steel for protection.
- The autoclave lid is tightened securely using the screw cap or bolts.
Step 4: Heating in an Oven or Furnace
The sealed autoclave is placed inside a heating oven, furnace, where it is heated to a specific temperature (often between 100°C and 300°C). The heat causes the liquid inside to evaporate and create high pressure.
Step 5: Chemical Reaction Under Pressure
As the temperature rises, the pressure inside increases. This high-pressure environment allows the chemicals to react and form new materials, such as nanomaterials, crystals, or advanced ceramics.
Step 6: Cooling and Opening
After the reaction, the autoclave can cool down naturally to avoid sudden pressure changes. Once it is safe:
- The lid is carefully opened.
- The final product (such as synthesized nanoparticles or crystals) is removed from the liner.
Why Is High Pressure Important?
In a hydrothermal autoclave, the combination of high temperature and pressure helps:
✔ Speed up chemical reactions.
✔ Produce materials with unique properties.
✔ Create uniform and high-quality nanomaterials.
Safety Precautions While Using an Autoclave
Since hydrothermal autoclaves operate at high pressure, safety is paramount:
✅ Always use high-quality materials for the autoclave.
✅ Never overfill the liner.
✅ Allow proper cooling before opening the lid.
✅ Wear gloves, goggles when handling chemicals.
Conclusion
A hydrothermal autoclave is a powerful tool for creating unique materials under controlled heat and pressure. By carefully sealing and heating the chemicals, researchers can develop advanced materials used in electronics, batteries, and nanotechnology. Understanding how it works helps ensure safe and efficient experiments.
Would you like to explore specific applications or modifications of a hydrothermal autoclave? Let us know!